The first tab on the GUI gives the material definition page. A minimum of one material must be
defined to obtain a solution. Any number of materials can be defined, even if all of the materials
are not actually used in cylinder definitions. Each material definition requires five input
parameters: the name, elastic modulus, Poisson ratio, thermal expansion coefficient (CTE), and
density. The name for each material must be unique and can have up to 10 characters. The
computed shear modulus and bulk modulus for each material are also displayed. Figure 5 shows
the material dialog page. Click on the figure for additional information.
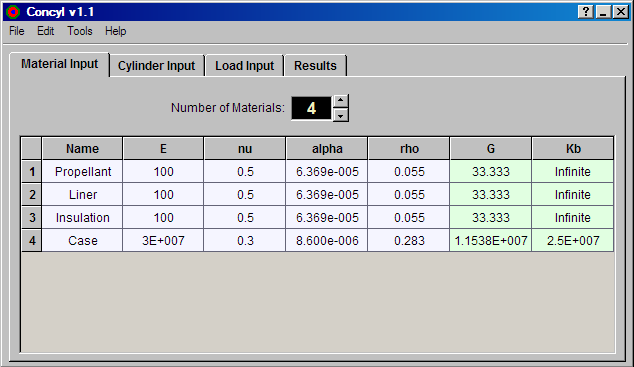
Figure 5. Material Definition Dialog Page
An isotropic material requires only two mechanical properties to define its elastic behavior. The
two properties required by Concyl are the elastic modulus and the Poisson ratio. The other
required material properties are the CTE and the density. The CTE relates the thermal strain to
the applied temperature, and the density is used to compute the cylinder mass. The table below
summarizes the properties required to define each material and the base units for each property.
Table 1. Required Material Input
|
Parameter
|
GUI Name
|
Units
|
Example Units
|
|
Elastic Modulus
|
E
|
F/L2
|
psi, Pa
|
|
Poisson Ratio
|
nu
|
unitless
|
-
|
|
CTE
|
Alpha
|
Temp-1
|
/°F, /°C
|
|
Density
|
rho
|
M/L3
|
lb/in3, kg/m3
|
Applicable Base Units:
F = force
M = mass
L = length
H = temperature
T = time
For isotropic materials, the shear modulus (G) and bulk modulus (K) are related to the elastic
modulus (E) and Poisson ratio (n) by the following formulas:
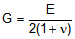 ,
, 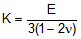
These formulas reveal that the Poisson ratio has an allowable range of -1 to 0.5. The 0 value
corresponds to a perfectly compressible material, and the 0.5 value corresponds to a perfectly
incompressible material.
The user can choose any units when entering the material properties. However, great care must
be taken to ensure that the material property units are mutually consistent and also consistent
with the units used to specify the applied loads. For example, if the elastic modulus units are psi,
then the density units must be lb/in3, and the applied pressure load units must also be psi.
Likewise, the radial dimensions of the cylinders must be entered in inches for consistency.

