QuatView uses
the following rotation conventions:
· Coordinate System Type: right handed
· Rotation Direction: counterclockwise is positive
· Transformation Direction: from reference Frame A (fixed) to Frame B
(rotating)
· Rotation Matrix Notation: row major with one row for each Frame B axis
unit vector. Rotation matrix is post multiplied by Frame A column vector to
get the rotated Frame B column vector.
· Quaternion Notation: [ q0, q1i, q2j, q3k ] (first component is scalar)
Other conventions in common use are left handed coordinate systems, clockwise
positive rotation, column major rotation matrix format, and quaternion numbering
with the scalar component last. The user must exercise care in applying the results
from QuatView to ensure that the above conventions are consistent with the user's
analysis conventions.
The relationships between the Euler angles, quaternion, and rotation matrix
generally depend on the choice of transformation direction and the coordinate
system type. Transformation direction really refers to the direction of the angle
measurements which can be referenced to the initial frame (Frame A) or the final
frame (Frame B). That is, the angles can be measured from Frame A to Frame B or
from Frame B to Frame A. The rotation matrix for one choice is simply the
transpose of the other choice. The quaternion for one choice is simply the complex
conjugate of the other. Choice of reference frame is described further in the
quaternion overview section here. The two different rotation matrix formats (row major or column major) are the
transpose of each other. The row major format is most commonly used in dynamic
simulation, while the column major format is most commonly used in computer
graphics. The row major format is meant to be post-multiplied by a column vector,
while the column major format is meant to be pre-multiplied by a row vector as
shown below where RR is the row major form and RC is the column major form.
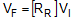 , row major
rotation matrix (used by QuatView and Direct3D)
, row major
rotation matrix (used by QuatView and Direct3D) 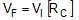 , column major rotation
matrix (used by OpenGL)
, column major rotation
matrix (used by OpenGL)VI has the vector components referenced to the initial unrotated frame (Frame A), and VF has
the vector components referenced to the final rotated frame (Frame B).